Hearing loss is a multifaceted condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Understanding the different levels of hearing loss is crucial for managing and mitigating its impact on daily life. This comprehensive guide explores the five levels of hearing loss, their symptoms, causes, and the various strategies and treatments available to improve quality of life.
Understanding Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is not a uniform experience; it varies significantly from person to person. Recognizing the different levels of hearing loss helps in tailoring appropriate interventions and support. Early detection and proper management can profoundly enhance one’s ability to communicate and engage with the world.
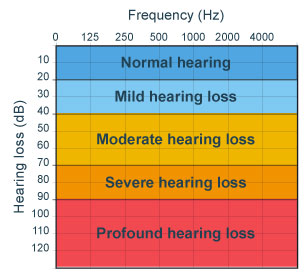
Image Source: Cochlea
1. Normal Hearing Loss
Definition of Normal Hearing Range
Normal hearing typically refers to the ability to hear sounds between 0 to 25 decibels (dB) across various frequencies. This range allows individuals to perceive both soft and loud sounds without difficulty.
How Normal Hearing is Measured
Normal hearing is measured using audiometric tests, which assess a person’s ability to hear sounds of different pitches and volumes. An audiogram plots the results, showing the threshold at which sounds become audible.
Signs of Normal Hearing in Daily Life
Individuals with normal hearing can effortlessly engage in conversations, even in noisy environments. They can hear soft sounds like a whisper or the rustling of leaves and distinguish between various background noises without strain.
Maintaining Healthy Hearing
Protecting normal hearing involves avoiding prolonged exposure to loud noises, using ear protection when necessary, and maintaining overall ear health through regular check-ups and hygiene practices.
2. Mild Hearing Loss
What is Mild Hearing Loss?
Mild hearing loss occurs when an individual has difficulty hearing sounds between 26 to 40 dB. This level of hearing loss may affect the clarity of speech, especially in noisy environments.
Common Causes of Mild Hearing Loss
Mild hearing loss can be caused by age-related changes, prolonged exposure to loud noises, ear infections, or obstructions such as earwax buildup.
Symptoms and Daily Impact
Difficulty Hearing Soft Sounds
People with mild hearing loss may struggle to hear soft sounds, such as whispers or distant conversations. This can make it challenging to follow conversations, particularly in quiet settings.
Struggling with Background Noise
Background noise can further complicate hearing, making it hard to distinguish speech from other sounds. This often leads to increased effort and fatigue during social interactions.
Strategies for Coping with Mild Hearing Loss
Lifestyle Adjustments
Simple adjustments, such as reducing background noise, using visual cues, and positioning oneself closer to the sound source, can significantly improve communication.
Use of Assistive Listening Devices
Assistive listening devices, like personal amplifiers and specialized telephones, can enhance hearing ability and reduce the strain of listening in various environments.
3. Moderate Hearing Loss
Defining Moderate Hearing Loss
Moderate hearing loss is characterized by difficulty hearing sounds between 41 to 70 dB. This level of hearing loss significantly impacts the ability to follow conversations and understand speech at normal volumes.
How Moderate Hearing Loss is Diagnosed
Moderate hearing loss is diagnosed through comprehensive audiometric testing, which evaluates hearing across different frequencies and intensities. Audiologists use these tests to determine the extent of hearing loss and recommend appropriate interventions.
Everyday Challenges
Understanding Conversations at Normal Volume
People with moderate hearing loss often find it challenging to understand speech at normal volumes. They may need to ask others to repeat themselves frequently or speak louder.
Increased Fatigue from Listening Efforts
The effort required to hear and understand conversations can lead to significant listening fatigue, affecting concentration and overall well-being.
Treatment Options and Aids
Hearing Aids and Their Benefits
Hearing aids are a common solution for moderate hearing loss. These devices amplify sounds, making it easier to hear and understand speech. Modern hearing aids come with various features, such as noise reduction and directional microphones, to improve listening comfort and clarity.
Communication Strategies for Better Understanding
Adopting effective communication strategies, such as speaking clearly, facing the listener, and using gestures, can greatly enhance understanding and reduce frustration.
4. Severe Hearing Loss
Understanding Severe Hearing Loss
Severe hearing loss is defined as difficulty hearing sounds between 71 to 90 dB. This level of hearing loss profoundly impacts communication and daily activities.
Causes and Risk Factors
Severe hearing loss can result from genetic factors, prolonged exposure to loud noises, infections, or untreated middle ear problems. Age-related hearing loss also commonly progresses to this level.
Impact on Communication and Social Life
Reliance on Lip Reading and Visual Cues
Individuals with severe hearing loss often rely heavily on lip reading and visual cues to understand speech. This reliance can make communication challenging in low-light or visually obstructed situations.
Difficulty in Group Conversations
Participating in group conversations can be particularly difficult, as background noise and multiple speakers can overwhelm the limited hearing capacity.
Advanced Hearing Solutions
Powerful Hearing Aids
Powerful hearing aids designed for severe hearing loss provide significant amplification and advanced features to enhance hearing in various environments.
Cochlear Implants
Cochlear implants are an option for individuals who do not benefit from hearing aids. These devices bypass damaged parts of the ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve, providing a sense of sound.
5. Profound Hearing Loss
What Constitutes Profound Hearing Loss?
Profound hearing loss involves difficulty hearing sounds above 90 dB. Individuals with this level of hearing loss may not hear most sounds and heavily rely on other senses for communication.
Identifying the Symptoms
Inability to Hear Most Sounds
Profound hearing loss results in the inability to hear everyday sounds, such as traffic noise, alarms, and conversations, even at elevated volumes.
Dependence on Visual and Tactile Signals
Individuals with profound hearing loss often depend on visual signals, like lip reading and sign language, and tactile signals, such as vibrations, to communicate and stay aware of their environment.
Life with Profound Hearing Loss
Social and Emotional Effects
Profound hearing loss can lead to social isolation, as communication becomes extremely challenging. Emotional effects, such as frustration, anxiety, and depression, are common.
Adaptation Techniques
Adaptation techniques, including the use of assistive technology and communication strategies, can help individuals manage their hearing loss and maintain an active lifestyle.
Technological and Medical Interventions
Cochlear Implants and Assistive Devices
Cochlear implants offer a viable solution for many with profound hearing loss. Additional assistive devices, such as vibrating alarms and captioning services, further enhance daily living.
Sign Language and Other Communication Methods
Learning sign language and other visual communication methods can provide effective ways to interact and engage with others, fostering a sense of community and support.
Diagnosing and Monitoring Hearing Loss
How Hearing Tests Work
Hearing tests involve a series of evaluations to determine the type and extent of hearing loss. These tests may include pure-tone audiometry, speech testing, and tympanometry.
Importance of Regular Hearing Check-Ups
Regular hearing check-ups are essential for early detection and management of hearing loss. They help track changes in hearing ability and ensure timely intervention.
Tools and Techniques for Monitoring Hearing Health
Modern tools, such as smartphone apps and home hearing test kits, allow individuals to monitor their hearing health regularly. Audiologists also use advanced diagnostic equipment for accurate assessments.
When to Seek Professional Help
Seek professional help if you notice any signs of hearing loss, such as difficulty understanding speech, needing to increase the volume on electronic devices, or experiencing ringing in the ears.
Living with Hearing Loss: Tips and Advice
Building a Support Network
Building a strong support network of family, friends, and professionals is vital for managing hearing loss. Support groups can provide emotional support and practical advice.
Effective Communication Strategies
Adopting effective communication strategies, such as using clear speech, maintaining eye contact, and reducing background noise, can improve interactions and reduce misunderstandings.
Tips for Clearer Conversations
Position yourself in well-lit areas, ask others to face you when speaking, and use assistive listening devices to enhance your hearing and improve conversation quality.
Using Technology to Enhance Hearing
Modern technology offers various solutions, such as hearing aids with Bluetooth connectivity, smartphone apps, and other assistive devices, to improve hearing and communication.
Emotional and Psychological Support
Dealing with hearing loss can take an emotional toll. Seeking psychological support, such as counseling and joining support groups, can help manage the emotional aspects of hearing loss.
Dealing with the Impact on Mental Health
Hearing loss can lead to mental health challenges, including anxiety and depression. Addressing these issues through professional help and support networks is crucial for overall well-being.
Finding Support Groups and Resources
Support groups and online communities provide a platform for sharing experiences, gaining insights, and finding resources to manage hearing loss effectively.
Conclusion
Hearing loss affects people in varying degrees, from mild to profound. Understanding these levels helps in recognizing symptoms early and seeking appropriate interventions. Early detection and treatment can significantly improve quality of life. Seek help, use available resources, and stay informed about advancements in hearing technology to navigate the challenges of hearing loss effectively.
