TYPES AND CAUSE
Types of Hearing Loss – A Simple Guide by an Audiologist
There are three main types of hearing loss: Conductive, Sensorineural, and Mixed.
Conductive Hearing Loss
- Happens when there is a problem in the outer or middle ear.
- Sound waves cannot pass properly to the inner ear.
- Can often be treated with medicine or surgery.
Causes of Conductive Hearing Loss:
- Ear structure problems (present from birth or due to an accident).
- Benign tumors in the ear.
- Excess earwax blocking sound.
- Ear canal infections.
- Foreign objects stuck in the ear.
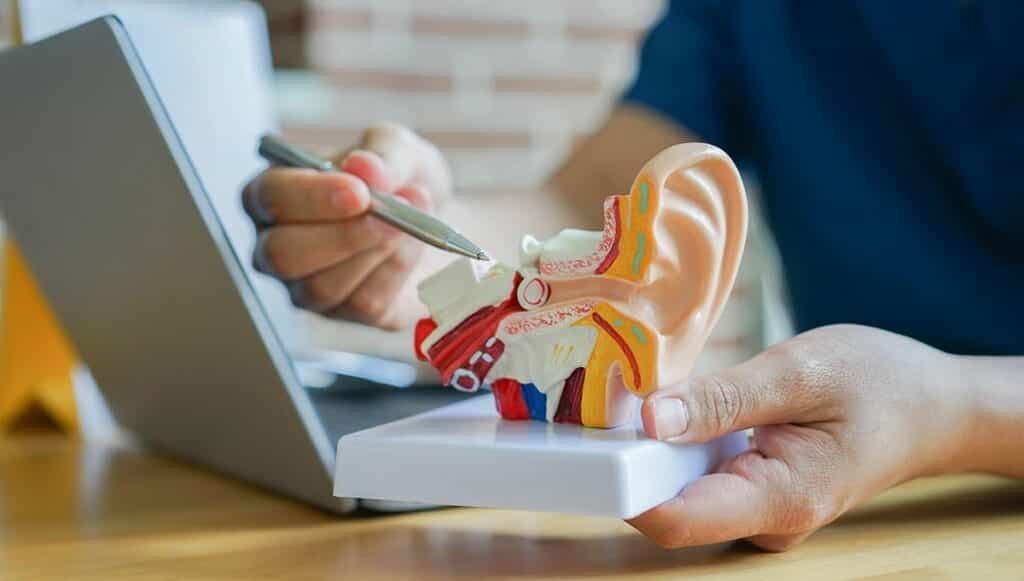
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
- Caused by damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve.
- Permanent hearing loss that cannot be reversed.
- Common in older adults and people exposed to loud noise.
Causes of Sensorineural Hearing Loss:
- Birth complications (lack of oxygen at birth).
- Genetic (hereditary) conditions.
- Viral or bacterial infections (rubella, herpes, syphilis, cytomegalovirus, meningitis).
- Ototoxic drugs (medications that harm hearing).
- Loud noise exposure over time or sudden loud explosions.
- Head or ear injuries.
Mixed Hearing Loss
- A combination of Conductive and Sensorineural hearing loss.
- Issues exist in both the outer/middle ear and the inner ear.
- Requires a detailed diagnosis by an Audiologist to determine the right treatment.

book a call
Take Action!
- If you notice hearing difficulties, consult an Audiologist for proper diagnosis and treatment.
- Early detection can prevent further hearing damage.
- Hearing aids or medical treatment can help improve quality of life.
FAQs
While stress itself doesn’t cause hearing loss, extreme stress can lead to temporary hearing issues, tinnitus, or worsen existing hearing conditions.
Yes, excessive earwax buildup can block sound and cause temporary conductive hearing loss, which is reversible when the blockage is removed.
Yes, genetic hearing loss can be present at birth (congenital) or develop later in life due to inherited conditions.
Yes, infections like otitis media (ear infection), meningitis, measles, and mumps can damage the ear structures and lead to temporary or permanent hearing loss.
Yes, prolonged exposure to loud noises (above 85 dB) can permanently damage the hair cells in the cochlea, leading to noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL).
Yes, this is called unilateral hearing loss, which can result from infections, trauma, tumors (acoustic neuroma), or sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSHL).
Mixed hearing loss occurs when both conductive and sensorineural hearing loss happen together. Common causes include:
• Aging combined with ear infections.
• Chronic ear infections leading to inner ear damage.
• Head injuries affecting both middle and inner ear structures.
SNHL results from damage to the inner ear or auditory nerve due to:
• Aging (presbycusis) – Natural deterioration of hair cells in the cochlea.
• Noise exposure – Loud music, machinery, gunfire, or explosions.
• Genetic factors – Hereditary conditions affecting hearing.
• Certain medications (ototoxic drugs) – Antibiotics, chemotherapy drugs, or high doses of aspirin.
• Head trauma – Injuries affecting the inner ear or brain.
• Diseases and infections – Meningitis, measles, or Meniere’s disease.
Conductive hearing loss occurs due to:
• Earwax buildup blocking the ear canal.
• Ear infections causing fluid buildup in the middle ear.
• Perforated eardrum from injury or loud noise.
• Otosclerosis – Abnormal bone growth in the middle ear.
• Foreign objects lodged in the ear.
